Advanced Professional Intercom Systems
Powering Unstoppable Performance: The RTS 50-Year Legacy
Whether on the ground or in orbit, RTS has spent the past 50 years redefining communication in the most critical moments. From powering live broadcasts and global events to supporting missions in space, our innovative solutions have become the gold standard for reliability and performance. As we celebrate our legacy, we’re also looking ahead—exploring groundbreaking technologies to transform the future of communication. Discover the RTS journey and what’s next for the industry...
RTS Wins Three Prestigious Awards at NAB Show 2025
RTS Celebrates Triple Honors for Breakthrough Innovation in Intercom and Cloud Communication Technology

Both RTS NOMAD Wireless Intercom and RTS Voice Over Cloud (RVOC) were recognized with Best of Show Awards by AVTechnology and Future plc, a global leader in media and content. Adding to the celebration, RVOC was also named an NAB Show 2025 Product of the Year—a top industry distinction.
Engineered for Excellence, Built to Perform
Our wireless intercoms, digital systems, and advanced software ensure seamless collaboration, even in the most critical environments.
Digital Matrix Intercom Systems
Designed for scalability and seamless integration, RTS digital matrix systems deliver unparalleled performance in any environment.
Wireless Intercom Systems
RTS wireless systems provide unmatched flexibility and clarity, ensuring reliable communication for dynamic, fast-paced productions.
Partyline Intercom Systems
Built for simplicity and durability, RTS partyline systems ensure clear communication across teams, no matter the scale.
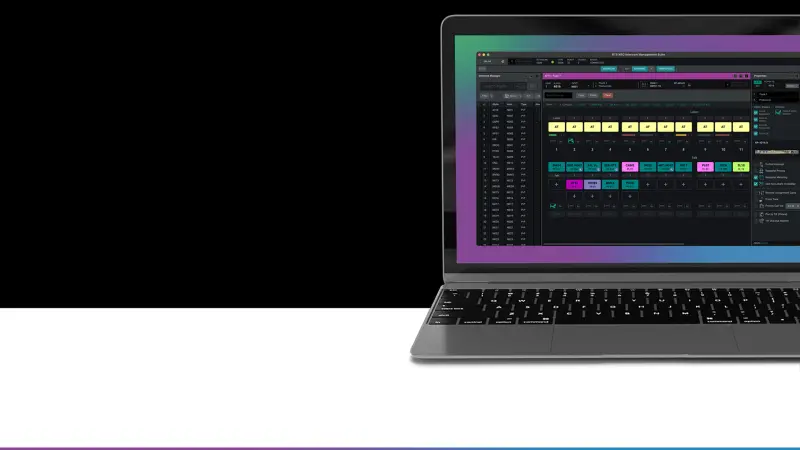
Software
Streamline operations with RTS software tools designed to optimize communication, integration, and system management.
Intercom Headsets
Lightweight yet robust, RTS headsets are engineered for comfort and precision in even the most demanding settings.
Cloud-Based Intercom Systems
Empowering teams with flexible, scalable, and secure cloud-based solutions, RTS brings communication into the future.
End-to-End Reliability and Innovation

Whether you're managing a live broadcast, coordinating a corporate event, or ensuring safety in critical environments, our solutions are designed to keep your team connected, productive, and efficient.
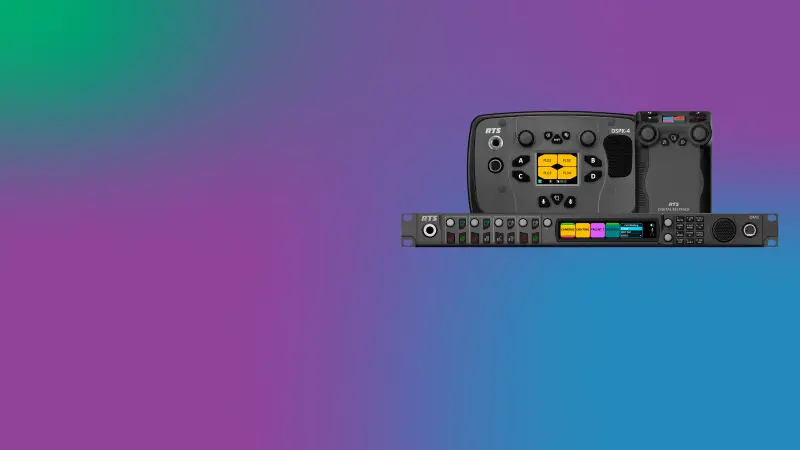
RTS Digital Partyline
A versatile and cost-effective solution, RTS Digital Partyline connects IP, digital, and analog devices with exceptional audio quality and an intuitive user experience. Unlike systems limited to analog, digital, or proprietary formats, RTS bridges all standards with cutting-edge interoperability.
Powered by OMNEO IP technology, including Dante for audio transport and AES70 for device control, the OMS (OMNEO Main Station) seamlessly integrates with RTS Digital Matrix products like ADAM, ODIN, and ROAMEO, as well as core Digital Partyline devices such as DBP (Digital Beltpack) and DSPK-4 (Digital Speaker Station).
RTS Digital Partyline offers an easy migration path from legacy equipment to IP-based infrastructure—preserving existing hardware investments without the complexity of a matrix system. Designed for scalability, it’s the ultimate hybrid communication tool for AV rentals, broadcasts, theaters, houses of worship, and more.
#theRTSdifference
Downloads

All the latest software & firmware releases from RTS in one convenient package. The latest version includes:
- DSPK4 support in AZedit , IPedit and ODIN and OMI
- NMOS proxy release (please find attached the Application note for RTS NMOS Proxy as well)
- Third party Dante Call light box support – the software was tested with Glen Sound and Studio Technologies Dante call light box. (already on demo at NAB)
- SDP - copy and paste support in IPedit introduced
Newsletter

Subscribe to our monthly eNewsletter to stay informed with the latest innovations, stories, and promotions from RTS Intercom Systems.